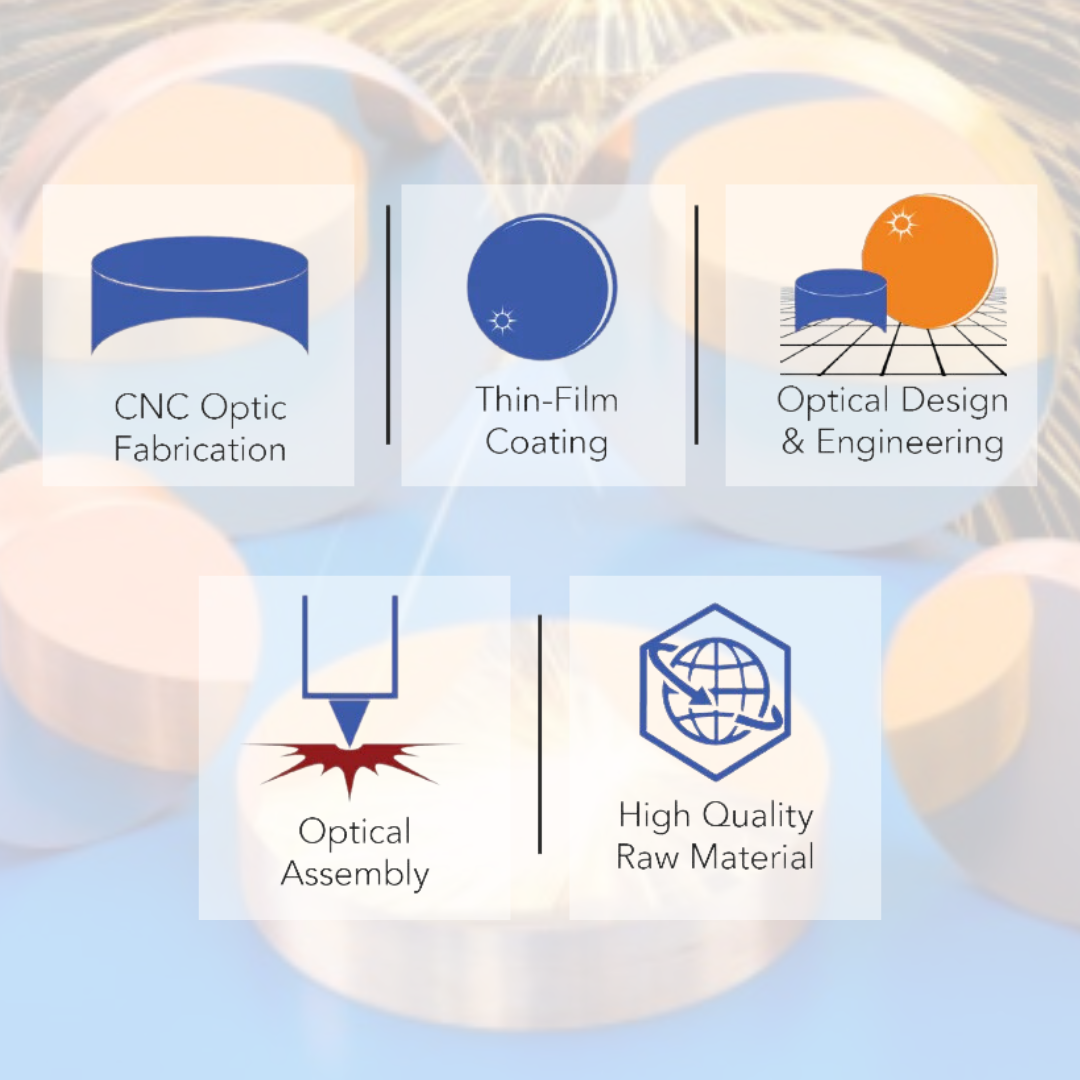
![]()
이산화탄소 코팅
박막 코팅 - ZnSe의 CO2 코팅
AR 10.6μm
10.6μm 및 633nm에서의 AR(HeNe)
10.6μm 및 650nm에서의 AR(다이오드)
10.6μm 및 633-650nm에서 빔 결합기
10.6μm에서 빔 스플리터(50%)
10.6μm에서 부분 반사경
AR 8μm ~ 128μm > 99%T
AR 3μm ~ 14μm > 95% T
AR 2.94μm >99.7% T
AR 2.5μm ~ 5μm > 99% T

Si 상의 Co2 코팅
실리콘의 CO2 코팅
00 10.6μm에서 위상 시프트 미러
10.6μm에서 900 위상 시프트 미러
10.6μm 및 VIS에서 향상된 은
적외선 코팅
게르마늄의 적외선 코팅
아연 셀렌화물의 적외선 코팅
황화아연 멀티스펙트럼의 적외선 코팅
갈륨비소의 적외선 코팅
실리콘에 적외선 코팅
다양한 금속 및 유리의 반사 코팅
박막 코팅
ZnSe의 CO2 코팅
AR 10.6μm
10.6μm 및 633nm에서의 AR(HeNe)
10.6μm 및 650nm에서의 AR(다이오드)
10.6μm 및 633-650nm에서 빔 결합기
10.6μm에서 빔 스플리터(50%)
10.6μm에서 부분 반사경
실리콘의 CO2 코팅
00 10.6μm에서 위상 시프트 미러
10.6μm에서 900 위상 시프트 미러
10.6μm 및 VIS에서 향상된 은
적외선 코팅
게르마늄의 적외선 코팅
아연 셀렌화물의 적외선 코팅
황화아연 멀티스펙트럼의 적외선 코팅
갈륨비소의 적외선 코팅
실리콘에 적외선 코팅
다양한 금속 및 유리의 반사 코팅.
APC: 코팅 코드 정의, 기능
AR - 반사 방지
AR,BBAR - 광대역 AR
AR,DBTR - 듀얼 밴드 전반사기
AR,TR - 전반사체
B/S - 광범위한 스펙트럼
B/S, DICH - 넓은 스펙트럼 이색성
BBAG 광대역 안티 G
BBAR - 광대역 반사 방지
BBAR,AR - 광대역 반사 방지 / 반사 방지
BBAR,DBAR - 광대역 반사 방지 / 듀얼 밴드 반사 방지
BBB/S
BBPR - 광대역 부분 반사경
BBTR - 광대역 총 반사경
BBTR,BBAR - 광대역 전반사 / 광대역 무반사
BBTR, BBAR, AR
DBAR - 듀얼 밴드 반사 방지
DBAR,TR, DBBAR, DBBF, DBBTR, DBTR, 필터
IR
편광판, PR, QBAR, RPR45, RPR90, TBAR, TBBAR,
TBPR, TBTR, TR, TR, AR, TR, BBAR, TR, DBAR, TR/IR