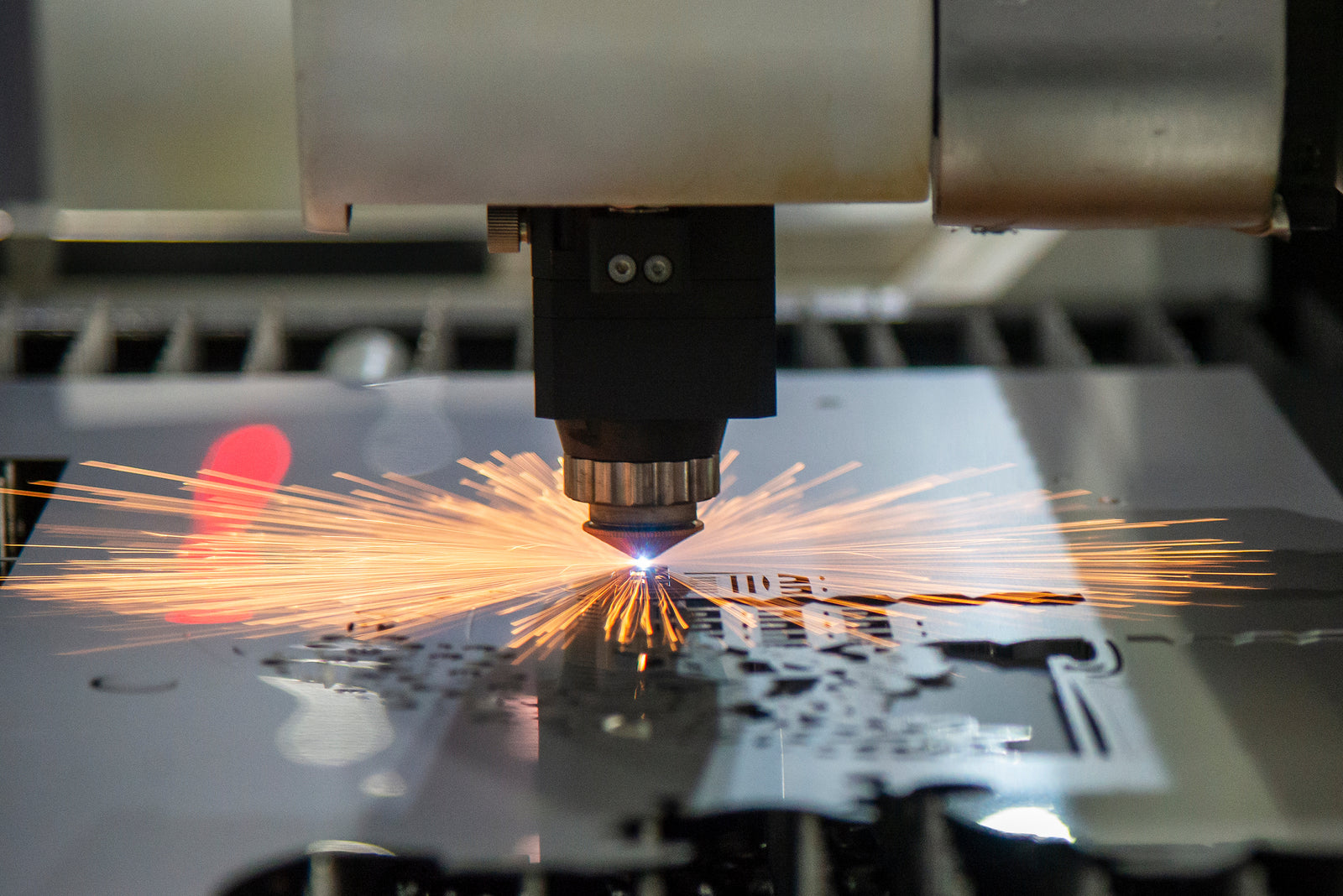
Among the types of laser systems available today, fiber laser machines have garnered significant attention for their superior performance in various applications. While your initial investment in a fiber laser may seem high, they typically offer low operating and maintenance costs. Let's break down the technology and examine how they compare to traditional CO2 laser machines.
How Fiber Laser Machines Work
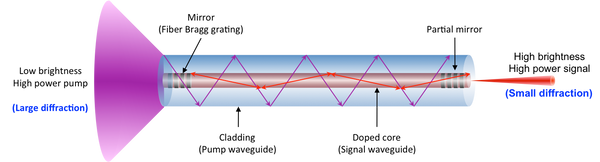
Fiber lasers belong to the solid-state laser group, utilizing an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as Erbium, Ytterbium, Neodymium, or Dysprosium as the active medium. The core mechanism involves pumping diode light into the fiber, triggering the doped fiber to concentrated light at a specific wavelength. This light is then amplified within the fiber, resulting in a highly focused laser beam.
The unique aspect of fiber lasers is their ability to produce an extremely fine and precise laser beam, which is ideal for cutting, engraving, and marking a wide range of materials with unparalleled accuracy. The fiber's structure naturally guides the laser beam, ensuring minimal beam divergence and allowing for high precision even over long distances.
Applications of Fiber Laser Machines

Fiber laser machines have found applications across various industries, thanks to their precision, efficiency, and versatility. Some of the key applications include:
- Metal Cutting and Engraving: From automotive manufacturing to jewelry design, fiber lasers are used to cut, engrave, and mark metals, offering clean cuts and detailed engravings on stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more.
- Medical Devices: The precision of fiber lasers is essential for creating intricate components in medical devices, such as stents and implants.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Fiber lasers are employed in the electronics industry to mark circuit boards and engrave barcodes, serial numbers, and logos.
- Laser Welding: Fiber laser welding is used in various sectors to provide high speed and efficiency, and low heat distortion.
Fiber Laser vs. CO2 Laser Machines
While both fiber and CO2 lasers are powerful tools in material processing, they have distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. Fiber lasers generally offer higher electrical efficiency compared to CO2 lasers. A fiber laser's efficiency can be over 30%, while CO2 lasers typically range around 10-20%. This makes fiber lasers more cost-effective in the long run, with lower energy consumption and operating costs. For metal cutting, fiber lasers tend to be faster and provide higher quality cuts, especially for thinner materials. However, CO2 lasers are better suited to work with a wider variety of materials, including plastics, wood, and glass due to their longer wavelength. Fiber lasers are known for their reliability and longevity, with minimal maintenance requirements. The solid-state design eliminates many of the moving parts and gas refills needed in CO2 laser systems, reducing downtime and extending the machine's lifespan.
Fiber laser machines have revolutionized industrial processing, offering unmatched precision, efficiency, and quality. American Photonics offers the replacement parts you need including lens assemblies, protective windows, nozzles, and other accessories. As technology continues to advance, we can expect fiber lasers to play an increasingly vital role in manufacturing, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in precision cutting, engraving, and marking.