![]()
Co2 Coating
Thin Film Coatings - CO2 Coatings on ZnSe
AR at 10.6μm
AR at 10.6μm and 633 nm (HeNe)
AR at 10.6μm and 650 nm (diode)
Beam Combiner at 10.6μm & 633-650nm
Beam Splitter (50%) at 10.6μm
Partial Reflector at 10.6μm
AR 8μm to 128μm > 99%T
AR 3μm to 14μm > 95% T
AR 2.94μm >99.7% T
AR 2.5μm to 5μm > 99% T

Co2 Coatings on Si
CO2 Coatings on Silicon
00 Phase Shift Mirror at 10.6μm
900 Phase Shift Mirror at 10.6μm
Enhanced Silver at 10.6μm and VIS
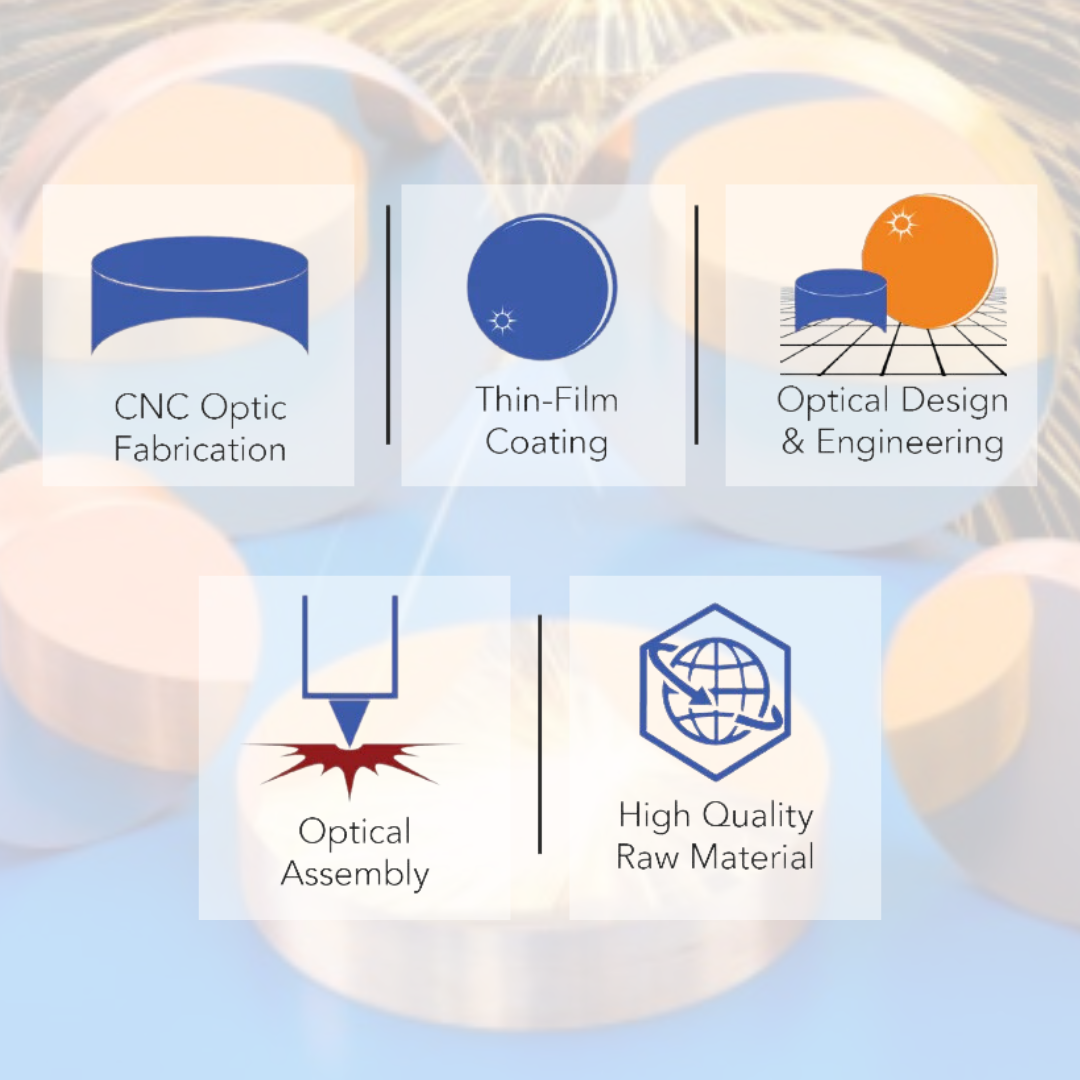
Infrared Coatings
Infrared Coatings on Germanium
Infrared Coatings on Zinc Selenide
Infrared Coatings on Zinc Sulfide Multispectral
Infrared Coatings on Gallium Arsenide
Infrared Coatings on Silicon
Reflective Coatings on Various Metals and Glass
Thin Film Coatings
CO2 Coatings on ZnSe
AR at 10.6μm
AR at 10.6μm and 633 nm (HeNe)
AR at 10.6μm and 650 nm (diode)
Beam Combiner at 10.6μm & 633-650nm
Beam Splitter (50%) at 10.6μm
Partial Reflector at 10.6μm
CO2 Coatings on Silicon
00 Phase Shift Mirror at 10.6μm
900 Phase Shift Mirror at 10.6μm
Enhanced Silver at 10.6μm and VIS
Infrared Coatings
Infrared Coatings on Germanium
Infrared Coatings on Zinc Selenide
Infrared Coatings on Zinc Sulfide Multispectral
Infrared Coatings on Gallium Arsenide
Infrared Coatings on Silicon
Reflective Coatings on Various Metals and Glass.
APC: Coating Codes Definitions, Capabilities
AR - Anti Relective
AR,BBAR - Broad Band AR
AR,DBTR - Dual Band Total Reflector
AR,TR - Total Reflector
B/S - Broad Spectrum
B/S, DICH - Broad Spectrum Dichroic
BBAG BROAD BAND ANTI G
BBAR - Broad Band Anti Reflective
BBAR,AR - Broad Band Anti Reflective / Anti Reflective
BBAR,DBAR - Broad Band Anti Reflective / Dual Band Anti Reflective
BBB/S
BBPR - Broad Band Partial Reflector
BBTR - Broad Band Total Reflector
BBTR,BBAR - Broad Band Total Reflector / Broad Band Anti Reflective
BBTR,BBAR,AR
DBAR - Dual Band Anti Reflective
DBAR,TR , DBBAR, DBBF, DBBTR, DBTR, Filter
IR
Polarizer, PR, QBAR, RPR45, RPR90, TBAR, TBBAR,
TBPR, TBTR, TR, TR,AR, TR,BBAR, TR,DBAR, TR/IR