![]()
Recubrimiento de Co2
Recubrimientos de película delgada - Recubrimientos de CO2 sobre ZnSe
RA a 10,6 μm
AR a 10,6 μm y 633 nm (HeNe)
AR a 10,6 μm y 650 nm (diodo)
Combinador de haz a 10,6 μm y 633-650 nm
Divisor de haz (50 %) a 10,6 μm
Reflector parcial a 10,6 μm
AR 8 μm a 128 μm > 99 %T
AR 3 μm a 14 μm > 95 % T
RA 2,94 μm >99,7 % T
AR 2,5 μm a 5 μm > 99 % T

Recubrimientos de Co2 sobre Si
Recubrimientos de CO2 sobre Silicio
00 Espejo de cambio de fase a 10,6 μm
Espejo de cambio de fase 900 a 10,6 μm
Plata mejorada a 10,6 μm y VIS
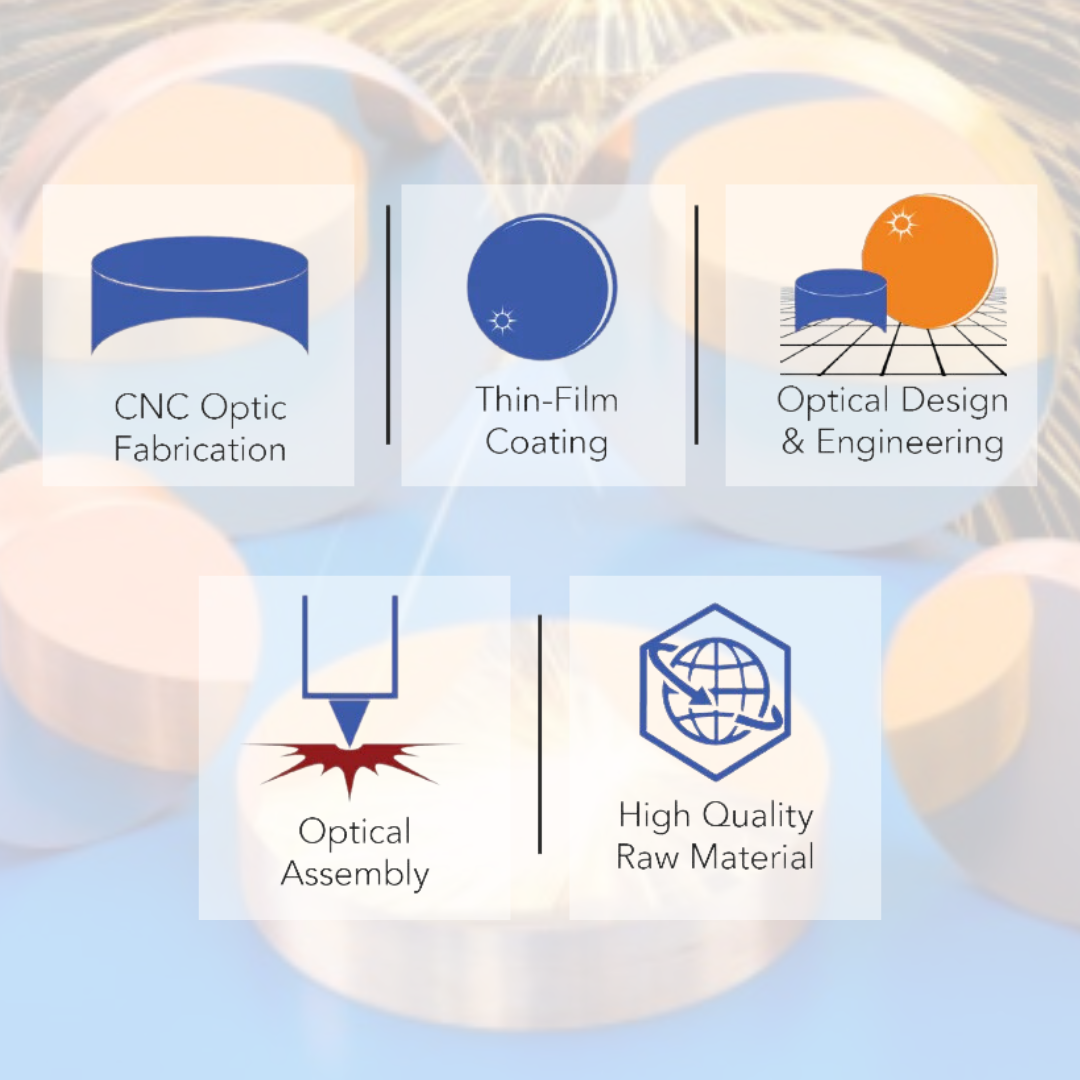
Recubrimientos infrarrojos
Recubrimientos infrarrojos en germanio
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre seleniuro de zinc
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre sulfuro de zinc multiespectral
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre arseniuro de galio
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre silicio
Revestimientos reflectantes en varios metales y vidrio
Recubrimientos de película delgada
Recubrimientos de CO2 sobre ZnSe
RA a 10,6 μm
AR a 10,6 μm y 633 nm (HeNe)
AR a 10,6 μm y 650 nm (diodo)
Combinador de haz a 10,6 μm y 633-650 nm
Divisor de haz (50 %) a 10,6 μm
Reflector parcial a 10,6 μm
Recubrimientos de CO2 sobre Silicio
00 Espejo de cambio de fase a 10,6 μm
Espejo de cambio de fase 900 a 10,6 μm
Plata mejorada a 10,6 μm y VIS
Recubrimientos infrarrojos
Recubrimientos infrarrojos en germanio
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre seleniuro de zinc
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre sulfuro de zinc multiespectral
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre arseniuro de galio
Recubrimientos infrarrojos sobre silicio
Recubrimientos reflectantes en varios metales y vidrio.
APC: definiciones de códigos de recubrimiento, capacidades
AR - Antirreflectante
AR,BBAR - Banda ancha AR
AR,DBTR - Reflector total de doble banda
AR,TR - Reflector total
B/S - Amplio Espectro
B/S, DICH - dicroico de amplio espectro
BBAG BANDA ANCHA ANTI G
BBAR - Antirreflectante de banda ancha
BBAR,AR - Banda ancha antirreflectante / antirreflectante
BBAR, DBAR - Antirreflejos de banda ancha / Antirreflejos de doble banda
BBB/S
BBPR - Reflector parcial de banda ancha
BBTR - Reflector total de banda ancha
BBTR,BBAR - Reflector total de banda ancha / Antirreflectante de banda ancha
BBTR,BBAR,AR
DBAR - Doble banda antirreflectante
DBAR,TR, DBBAR, DBBF, DBBTR, DBTR, filtro
infrarrojos
Polarizador, PR, QBAR, RPR45, RPR90, TBAR, TBBAR,
TBPR, TBTR, TR, TR, AR, TR, BBAR, TR, DBAR, TR/IR